What are Zonal Councils?
- Zonal councils have been established by the Parliament to promote interstate cooperation and coordination.
- They are statutory bodies established under the States Reorganisation Act 1956 and not constitutional bodies.
- They are only deliberative and advisory bodies
How many Zonal Councils are there?
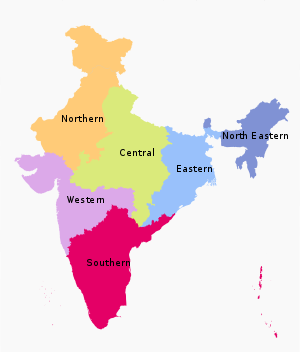
There are 5 five Zonal councils namely:
- The Northern Zonal Council, comprising the States of Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu & Kashmir, Punjab, Rajasthan, National Capital Territory of Delhi and Union Territory of Chandigarh.
- The Central Zonal Council, comprising the States of Chhattisgarh, Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh.
- The Eastern Zonal Council, comprising the States of Bihar, Jharkhand, Orissa, and West Bengal.
- The Western Zonal Council, comprising the States of Goa, Gujarat, Maharashtra and the Union Territories of Daman & Diu and Dadra & Nagar Haveli.
- The Southern Zonal Council, comprising the States of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu and the Union Territory of Puducherry.
The North Eastern States i.e. (i) Assam (ii) Arunachal Pradesh (iii) Manipur (iv) Tripura (v) Mizoram (vi) Meghalaya (vii) Sikkim and (viii) Nagaland are not included in the Zonal Councils and their special problems are looked after by the North Eastern Council, set up under the North Eastern Council Act, 1972.
What is the composition of Zonal Councils?
- Chairman – The Union Home Minister is the Chairman of each of these Councils.
- Vice Chairman – The Chief Ministers of the States included in each zone act as Vice-Chairman of the Zonal Council for that zone by rotation, each holding office for a period of one year at a time.
- Members- Chief Minister and two other Ministers as nominated by the Governor from each of the States and two members from Union Territories included in the zone.
- Advisers- One person nominated by the Planning Commission (which has been replaced by NITI Ayog now) for each of the Zonal Councils, Chief Secretaries and another officer/Development Commissioner nominated by each of the States included in the Zone.
- Union Ministers are also invited to participate in the meetings of Zonal Councils depending upon necessity.
What is the objective of zonal councils?
The main objectives of setting up of Zonal Councils are:
- Bringing out national integration.
- Arresting the growth of acute State consciousness, regionalism, linguism and particularistic tendencies.
- Enabling the Centre and the States to co-operate and exchange ideas and experiences.
- Establishing a climate of co-operation amongst the States for successful and speedy execution of development projects.
Thanks?