What is West Nile Virus?
-
West Nile Virus is a viral infection which typically spread by mosquitoes and results in neurological disease as well as death in people.
-
The Virus is the member of the flavivirus genus and belongs to the Japanese encephalitis antigenic complex of the family Flaviviridae.
-
It was first detected in a woman in the West Nile district of Uganda in 1937 and was later identified in birds (crows and Columbiformes) in the Nile delta region in 1953.
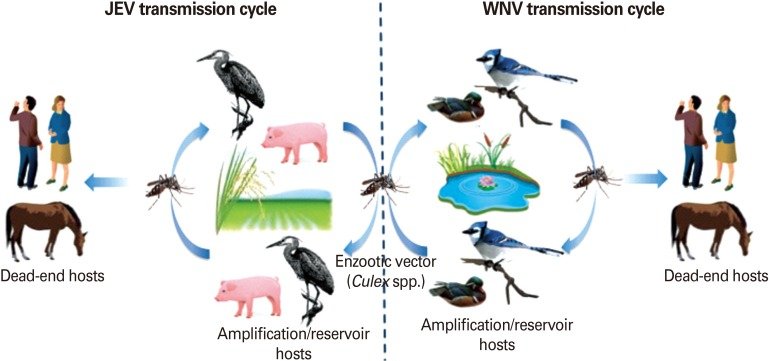
Spread of Disease
-
The disease spreads through mosquito bites.
-
Mosquitoes are infected when they feed on infected birds.
-
The virus then circulates in blood and multiplies.
-
The virus also travels to salivary glands from where it is injected into humans as well as animals through mosquito bites.
-
There have been no reports of human-to-human transmission through casual contact till date.
-
But a small proportion of human infections have reported through organ transplant, blood transfusions and breast milk while one case of transplacental.
Symptoms
-
People infected with WNV suffer from fever, headache, fatigue, body aches, nausea, vomiting, occasionally with a skin rash (on the trunk of the body) and swollen lymph glands.
-
In case of severe West Nile disease, the patient suffers from headache, high fever, neck stiffness, disorientation, stupor, coma, tremors, convulsions, muscle weakness and paralysis.
-
One in 150 persons infected with the virus will develop a severe form of the disease, according to the World Health Organisation (WHO).
-
There are no vaccines to prevent or medications to treat the infection.