Thermobaric Weapons or Vacuum Bomb:
-
Thermobaric weapons, also known as aerosol bombs, fuel air explosives, or vacuum bombs, use oxygen from the air for a large, high-temperature blast.
-
A thermobaric weapon causes significantly greater devastation than a conventional bomb of comparable size.
-
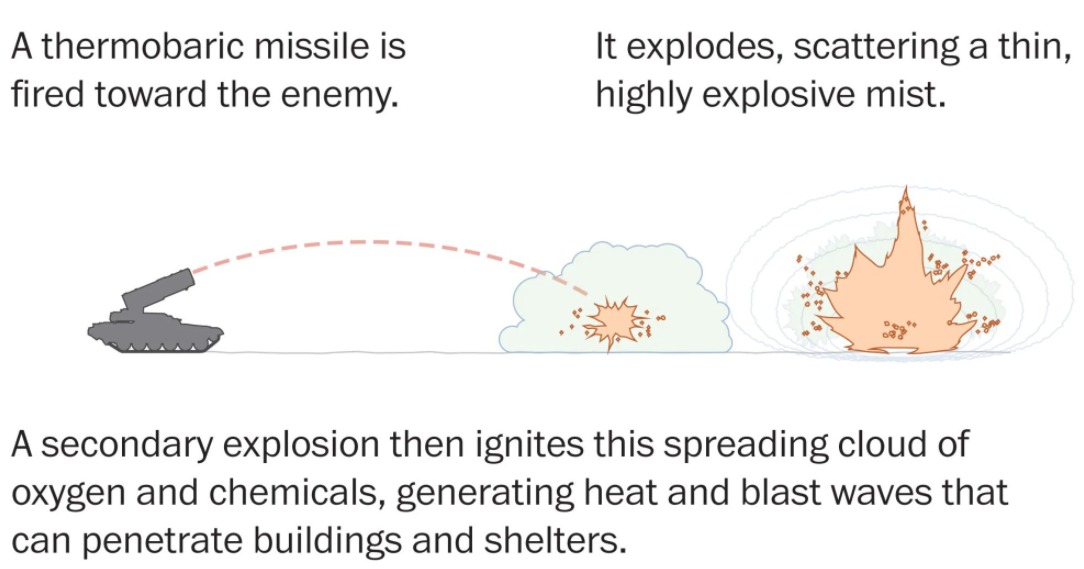
The weapons, which go off in two separate stages, can be fired as rockets from tank-mounted launchers or dropped from aircraft.
-
As they hit their target, a first explosion splits open the bomb’s fuel container, releasing a cloud of fuel and metal particles that spreads over a large area.
-
A second explosion then occurs, igniting the aerosol cloud into a giant ball of fire and sending out intense blast waves that can destroy even reinforced buildings or equipment and vaporize human beings.
-
Vacuum bombs are not prohibited by any international law or agreement, but their use against civilian populations in built-up areas, schools or hospitals, could attract action under the Hague Conventions of 1899 and 1907.
-
Hague Convention is any of a series of international treaties that were issued from international conferences held at The Hague in the Netherlands in 1899 and 1907.
-
They establish the laws and customs of war in the strict sense, by defining the rules that belligerents must follow during hostilities.