-
OPEC stands for Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries
-
Founded in 1960 in Bagdad
-
HQ : Vienna
-
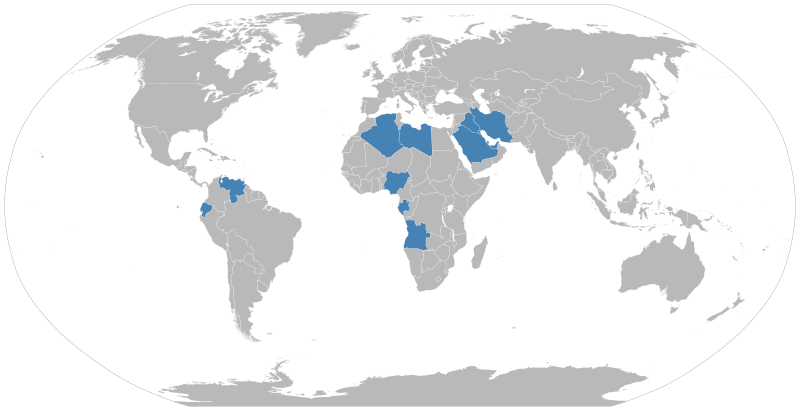
13 members
-
Algeria,
-
Angola,
-
Congo
-
Equatorial Guinea,
-
Gabon,
-
Iran,
-
Iraq,
-
Kuwait,
-
Libya,
-
Nigeria,
-
Saudi Arabia (the de facto leader),
-
United Arab Emirates, and
-
Venezuela.
-
OPEC sets production targets for its member nations and generally, when OPEC production targets are reduced, oil prices increase
-
OPEC decisions have come to play a prominent role in the global oil market and international relations
-
The OPEC Statute distinguishes between the Founder Members and Full Members (those countries whose applications for membership have been accepted by the Conference).
-
The Statute stipulates that “any country with a substantial net export of crude petroleum, which has fundamentally similar interests to those of Member Countries, may become a Full Member of the Organization, if accepted by a majority of three-fourths of Full Members, including the concurring votes of all Founder Members.”
-
The Statute further provides for Associate Members which are those countries that do not qualify for full membership, but are nevertheless admitted under such special conditions as may be prescribed by the Conference.
-
The non-OPEC countries which export crude oil are termed as OPEC plus countries.
-
OPEC plus countries include Azerbaijan, Bahrain, Brunei, Kazakhstan, Malaysia, Mexico, Oman, Russia, South Sudan and Sudan.
-
Map (Taken from Wikipedia. Not up to scale. For educational purpose only):