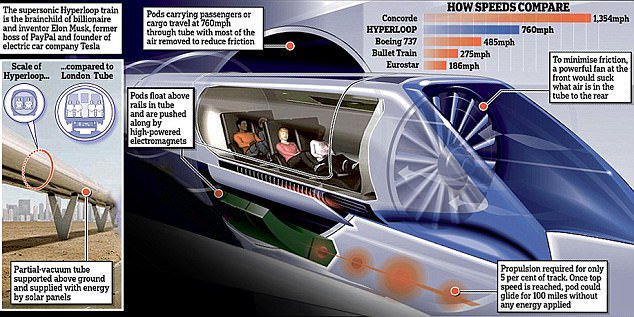
What is Hyperloop Technology?
- Theoretical concept of hyperloop is mooted by maverick techno-entrepreneur Elon Musk in 2013.
- Hyperloop technology promises to move people and goods through low-pressure tubes far faster than commercial air travel, within earthly confines, of course.
- In hyperloop transportation, custom-designed capsules or pods are expected to zip smoothly through continuous steel tubes which are held at partial vacuum.
- The pod which sandwiches the passenger compartment between an air compressor upfront and a battery compartment in the rear is supported by air caster skis at the bottom.
- The skis float on a thin layer of air provided under high pressure, eliminating rolling resistance and allowing for movement of the pods at high speeds. These capsules are expected to be driverless with estimated speeds of 1,000 km/h.
- Linear induction motors that are placed along the tube control the speed of the pod. Electronically-assisted acceleration and braking determines the speed of the capsule.
Why is it important?
Developments in traditional high speed railway technology have not made much progress in recent years. From steam to diesel to electric, locomotives have come up against the physical constraints of weight and drag. Frictional losses too come into play when a vehicle relies on wheels. As speeds accelerate, mechanical wear and tear leads to high maintenance costs. Maglev (magnetic levitation), which was expected to provide a solution has not gained traction. High-power consumption, accidents and technical challenges have hampered its progress.
In Hyperloop, during the pod’s journey, an inlet fan and compressor push high pressure air from the nose to tail. This action and the partial vacuum which eliminates most of the drag, boosts the speed. Low power consumption and reliance on existing infrastructure after re-engineering, are big positives.
Advantages
- Hyperloop is two-to-three times faster than fastest high-speed rail and claimed to have speeds even greater than commercial air travel.
- It has smaller civil engineering footprint, with no direct emissions or noise compared to railways.
- Hyperloop system’s capital cost per mile is 60% that of high-speed rail, and is less expensive to operate.
- Furthermore, Hyperloop departures could happen with a low frequency of a pod every 20 seconds which is not possible in railways.
Challenges
- It requires heavy investments and therefore effective public and private sector coordination is prerequisite for implementing it.
- It consumes high-power compared to railways.
- Technical challenges and accidents may hamper its progress.
Why in news?
- AP government is planning to connect Vijayawada and Amaravati by a Hyperloop Project.
- The Virgin Group led by Richard Branson has signed an intent agreement with Maharashtra Government to build world’s first hyperloop
transportation system between Mumbai and Pune.