-
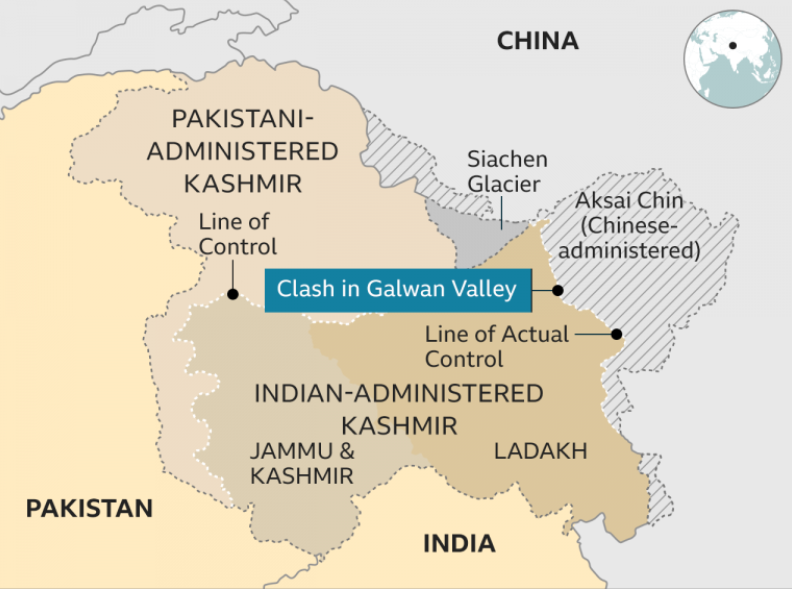
The Galwan River flows from the disputed Aksai Chin region administered by China to the Ladakh region of India.
-
It originates near the caravan campsite Samzungling on the eastern side of the Karakoram range and flows west to join the Shyok River.
-
The point of confluence is 102 km south of Daulat Beg Oldi.
-
Shyok River itself is a tributary of the Indus River, making Galwan a part of the Indus River system.
-
The narrow valley of the Galwan River as it flows through the Karakoram mountains has been a flashpoint between China and India in their border dispute.
-
Strategic importance of Galwan River Valley (GRV):
-
The Galwan River is the highest ridgeline and it allows the Chinese to dominate the Shyok route passes, which is close to the river.
-
It lies along the western sector of the LAC and close to Aksai Chin, a disputed area claimed by India but controlled by China.
-
Why tensions suddenly rose in this area?
-
India is trying to construct a feeder road emanating from Darbuk-Shyok Village – Daulat Beg Odi road (DS-DBO road).
-
This road runs along the Shyok River and is the most critical line of communications close to LAC.
-
Hence, Chinese were keen on controlling this area as they fear that the Indian side could end up threatening their position on the Aksai Chin plateau by using the river valley.