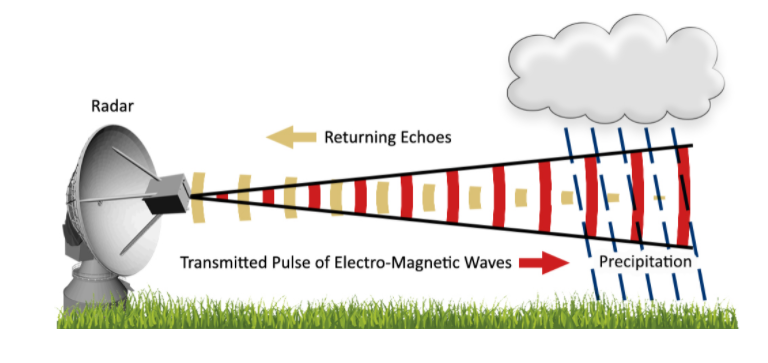
Radar (Radio Detection and Ranging):
-
It is a device which uses electromagnetic waves in the microwaves region to detect location (range & direction), altitude, intensity and movement of moving and non-moving objects.
Doppler radar:
-
Doppler radar is an observational tool used for precisely monitoring and predicting severe weather events such as hailstorms, thunder storms, cyclones and tornados.
-
It uses Doppler effect by bouncing microwave signal off desired target to produce velocity data.
-
This data helps in analysing object’s motion by altered frequency of returned signal.
-
It mainly gives information about wind velocity and precipitation.
-
Doppler radar has radius of 250 km and helps in issuing forecasts two-three hours prior to severe weather conditions.
-
It can provide area specific rain and storm warnings which are beneficial for disaster management and emergency response, aviation and related services.
-
It can be used for wind speed measurements during cyclones and thunderstorms which is not possible in conventional weather radar.
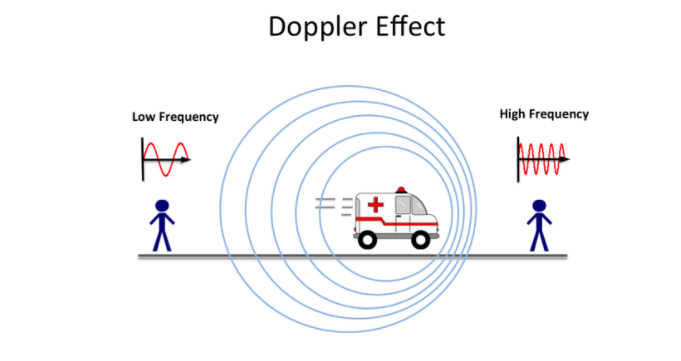
Doppler effect:
-
When the source and the signal are in relative motion to each other there is a change in the frequency observed by the observer. If they are moving closer frequency increases and vice versa.
-
It does this by bouncing a microwave signal off a desired target and analysing how the object’s motion has altered the frequency of the returned signal.
-
This variation gives direct and highly accurate measurements of the radial component of a target’s velocity relative to the radar.