Skip to content
- It is one of the most common orthopaedic birth defects where one or both feet are rotated inwards and downwards.
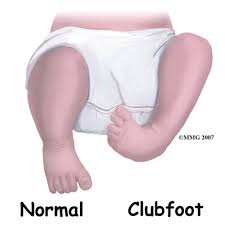
- It describes range of foot abnormalities usually present at birth in which your baby’s foot is twisted out of shape or position.
- In clubfoot, tissues connecting muscles to the bone (tendons) are shorter than usual.
- Causes: They are unknown (idiopathic), but it may be combination of genetics and environment.
- Symptoms of Clubfoot:
- Top of the foot is usually twisted downward and inward, increasing arch and turning heel inward.
- The foot may be turned so severely that it actually looks as if it’s upside down.
- The affected foot may be up to 1/2 inch (about 1cm) shorter than other foot. The calf muscles in affected leg are usually underdeveloped.
- Threats:
- It causes foot deformity, abnormality walking, callus, knock knees, or shortened legs.
- It can cause permanent disability if not treated early.
- This affects the child’s mobility and confidence.
- It occurs in about one in 1,000 newborns.
- In India, burden of disability affects more than 10 million people.
- Treatment:
- Ponseti method is initially used which involves moving foot into an improved position followed by casting, which is repeated at weekly intervals.
- Once the inward bending is improved, the Achilles tendon is often cut and braces are worn until age of four.
- Initially brace is worn nearly continuously and then just at night.
- In about 20% of cases further surgery is required.