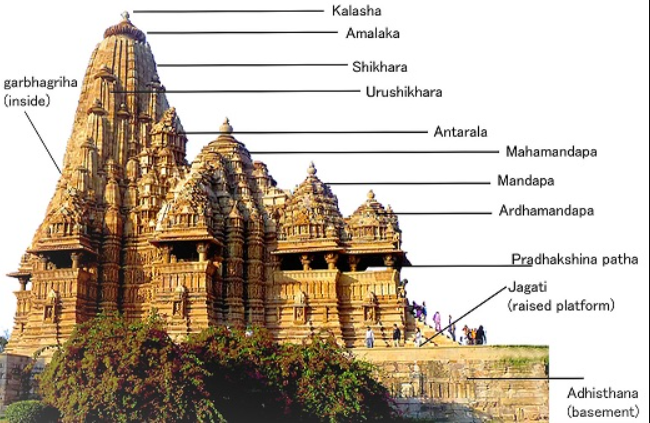
Basic elements of a Hindu Temple:
-
Garbhagriha:
-
Literally means womb-house.
-
It is a cave-like sanctum which houses the main icon of the temple.
-
In earlier times, it was a small cubicle with one entrance.
-
In later periods, it grew into a larger chamber.
-
-
Mandapa:
-
It is the entrance to the temple.
-
It could be a portico or a collonaded hall where worshippers stand.
-
-
Shikhara/Vimana:
-
Noticed from the 5th century CE.
-
It is a mountain-like spire on top.
-
In north India, it is called Shikhara and is curving in shape.
-
In the south, it is like a pyramidal tower and is called Vimana.
-

-
Amalaka:
-
Stone-like disc seen at the top of the temple.
-
Mostly found in north Indian temples.
-
-
Kalasha:
-
It is the topmost part of the temple.
-
Mainly seen in north Indian styles.
-
-
Antarala:
-
It is a vestibule between the Garbhagriha and the Mandapa.
-
-
Jagati:
-
This is common in north Indian temples and is a raised platform where devotees can sit and pray.
-
-
Vahana:
-
It is the vehicle of the main deity which along with the standard pillar or Dhvaj which are placed axially
-