What is Net Neutrality?
Net Neutrality means that telecom and Internet service providers must treat all data on the Internet equally, and not discriminate or charge differently by user, content, site, platform, or application.
Examples in Net Neutrality debate:
-
Facebook’s “Free Basics” or “internet.org“
-
Airtel Zero
Zero ratings: is a practice by which internet operators offer free data for specific applications
Free Basics: is an open platform that any developer can build something for regardless of who they are if they follow the basic rules. Such a product will be available for free to all subscribers of service in partnership with FB.
Benefits of sponsored data :
-
Increase the digital reach especially in developing countries like India where data charges are still high for its universal reach given the economic status of majority of the population.
-
Increased revenue for ISPs
-
Increased reach of government services.
All these benefits will help in enhancing capacity of the population and thus give an impetus to the economy.
Why opposition:
-
Violates the principle of net neutrality
-
Sponsored Data makes ISPs the gatekeepers of the internet traffic thus deciding which data the users should use or not
-
It discourages the spirit of innovation and entrepreneurship which has made the internet what it is today
What economics and politics suggest about net neutrality:
Economics-
-
As the Telecom service providers (TSPs) have paid heavy charges for spectrum via auctions, they are legal owners of it and are free to do whatever they like
-
TSPs are getting no share of revenue from Over-the-Top Service providers (like Facebook, Skype etc.) even though OTTs are using their network to operate and profit from
-
There will be no economic incentive for TSPs to expand their networks without a cut of profits from OTTs
-
OTTs are neither licensed, nor regulated, thus making it unfair for TSPs who not only have to pay heavy spectrum charges but also follow strict regulations
Politics-
-
In a recent survey, 77% citizens want govt. to protect net neutrality.
-
The internet has been declared to be a public utility by the US FCC and there are demands for the TRAI to do the same
-
Choosing what to and what not to access on the internet should be the users’ choice- not the TSP’s.
-
Moving away from net neutrality will cause balkanization of the internet and will stifle local entrepreneurship, innovation and open learning.
-
An open internet will encourage transparency and accountability among authorities and increases the democratic space available to citizens to have their grievances redressed.
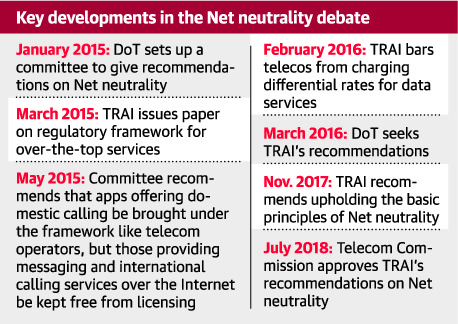
TRAI rules against differential pricing:
-
No discriminatory pricing for content-led data services
-
Reduced tariff for providing emergency services
-
Financial disincentives for contravention of said regulation
-
TRAI may review these regulations after 2 years
.png)

Good Read:
Related Questions:
-
“Economics suggests that policymakers should reject the concept of Net Neutrality and politics suggests that they should accept it.” Do you agree? Critically comment. (200 Words)
-
What do you understand by “net neutrality”? Do you think regulating internet has negative consequences? Examine. (200 Words)