Union Cabinet has approved National Digital Communications Policy-2018 (NDCP 2018). It also has re-designated Telecom Commission as Digital Communications Commission. It replaces existing National Telecom Policy-2012 to cater to the modern needs of the digital communications sector of India.
National Digital Communications Policy-2018 (NDCP 2018)
- It envisions supporting India’s transition to digitally empowered economy and society by fulfilling information and communications needs of citizens and enterprises.
- It strives to achieve this by establishing ubiquitous, resilient and affordable digital communications infrastructure and services.
- It is customer focused and application driven.
- It will help lead to new ideas and innovations after launch of advanced technology such as 5G, IOT, M2M, etc. which shall India’s govern telecom sector.
Key Objectives
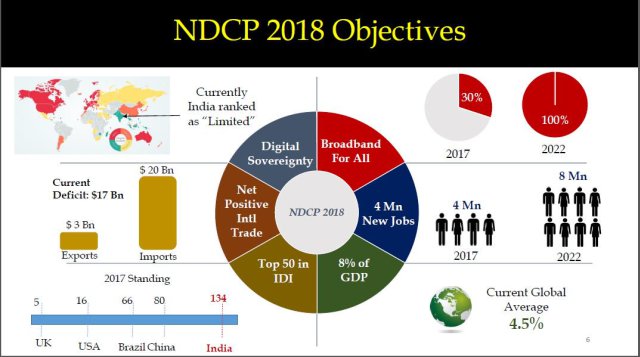
- Broadband for all.
- Creating four million additional jobs in Digital Communications sector.
- Enhancing contribution of Digital Communications sector to 8% of India’s GDP from ~ 6% in 2017.
- Propelling India to Top 50 Nations in ICT Development Index of ITU from 134 in 2017.
- Enhancing India’s contribution to Global Value Chains and
- Ensuring Digital Sovereignty.
These objectives are to be achieved by 2022.
Features
NDCP 2018 aims to
- Provide universal broadband connectivity at 50 Mbps to every citizen.
- Provide 1 Gbps connectivity to all Gram Panchayats by 2020 and 10 Gbps by 2022.
- Ensure internet connectivity to all uncovered areas.
- Attract investments of US $100 billion in Digital Communications Sector.
- Train 1 million manpower for building New Age Skill.
- Expand IoT ecosystem to 5 billion connected devices.
- Establish comprehensive data protection regime for digital communications that safeguards privacy, autonomy and choice of individuals
- Facilitate India’s effective participation in global digital economy;
- Enforce accountability through appropriate institutional mechanisms to assure citizens of safe and
- Secure digital communications infrastructure and services.
Strategy
NDCP 2018 advocates
- Establish National Digital Grid by creating National Fibre Authority.
- Establish Common Service Ducts and utility corridors in all new city and highway road projects.
- Create collaborative institutional mechanism between Centre, States and Local Bodies for Common Rights of Way, standardization of costs and timelines;
- Remove barriers to approvals.
- Facilitate development of Open Access Next Generation Networks.
Why such policy was needed?
- As the present technological world has entered into era of modern technological advancements in Telecom Sector such as 5G, Internet of things (loT), Machine to machine (M2M) communication etc.
- So, need was being felt to introduce customer focused and application driven policy for Indian Telecom Sector.
- This policy’s main intention was to serve as main pillar of Digital India by addressing emerging opportunities for expanding not only availability of telecom services but also telecom based services.
- Accordingly, new National Digital Communications Policy – 2018 has been formulated.