Challenges:
- Slow pace of negotiations on services trade liberalization as opposed to ‘higher priority’ being accorded to commitments to open up goods trade in the region.
- While it was decided that negotiations on trade in goods, trade in services, investment and other areas will be conducted in parallel to ensure a comprehensive and balanced outcome.
- No much progress in issues such as Intellectual Property Rights and investment liberalization.
‘RCEP Travel Card’: Idea mooted by India
- India is seeking support for its proposal on an ‘RCEP Travel Card’
- India is relatively strong in services with its vast pool of professionals including from sectors such as Information Technology, as well as in activities such as installation, trouble shooting, training, maintenance, investment management.
- Issues raised by other members: easing norms on temporary movement of people could lead to immigration of professionals from India and in turn loss of jobs for locals.
Suresh Prabhu Panel:
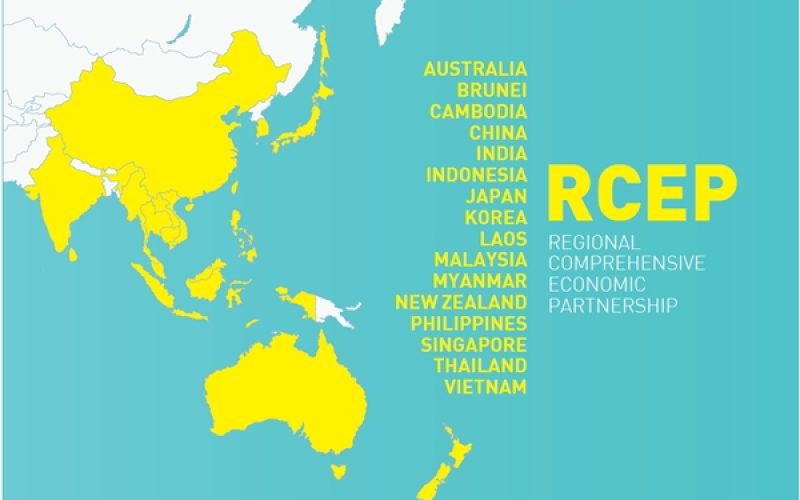
- Union Government has constituted four-member Group of Ministers (GoM) headed by Union Minister of Commerce and Industry Suresh Prabhu to decide on 16-member Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) negotiations.
- It was constituted to advise Prime Minister on whether to continue with or withdraw from RCEP negotiations.
- It has been mandated to find way forward from current deadlock over issues of joining RCEP or not.
- It will also help fine tune India’s strategy for the upcoming RCEP ministerial meet in August 2018 in Singapore.
India’s Concerns:
- There has been rising pressure on India to allow more market access to RCEP member countries including China and conclude negotiations by end of 2018.
- Several RCEP countries want India to open up its market for 92% of traded goods, while they are still reluctant to allow Indian skilled professionals greater access to their markets.
- India has maintained its position that it is ready to offer access for up to 85% of items, with deviations for countries such as Australia, New Zealand and China, with whom it does not have FTA.
- Besides, India also has trade deficit with 10 RCEP countries including China, South Korea and Australia, among others.
Source: