Context: According to a study, Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) is losing its stability and is very likely that AMOC will decline over the 21st century.
What is Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation(AMOC)?
AMOC is a large system of ocean currents. It is the Atlantic branch of the ocean conveyor belt or Thermohaline circulation (THC) and distributes heat and nutrients throughout the world’s ocean basins.
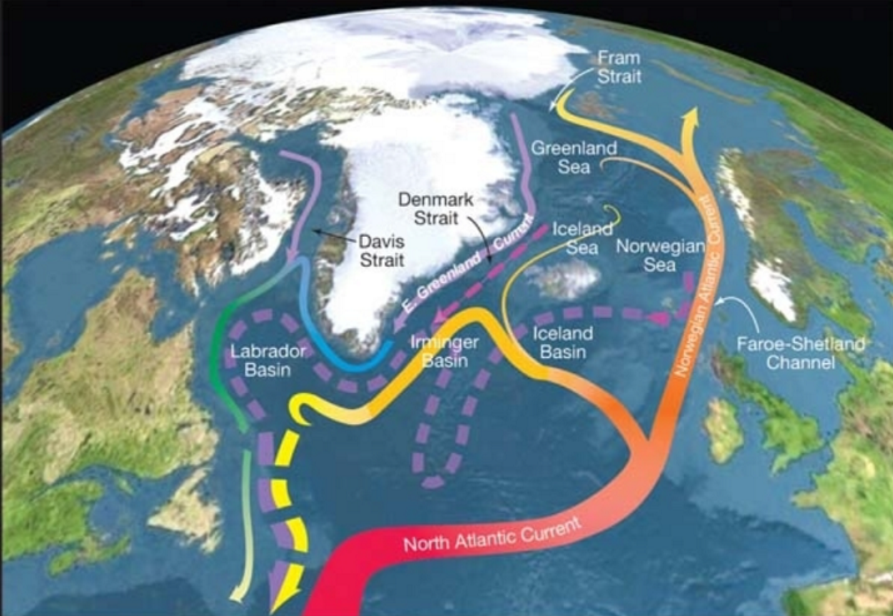
How does AMOC work? AMOC carries warm surface waters from the tropics towards the Northern Hemisphere, where it cools and sinks. It then returns to the tropics and then to the South Atlantic as a bottom current. From there it is distributed to all ocean basins via the Antarctic circumpolar current.
What happens if AMOC collapses?
-
Gulf Stream, a part of the AMOC, is a warm current responsible for mild climate at the Eastern coast of North America as well as Europe. Without a proper AMOC and Gulf Stream, Europe will be very cold.
-
AMOC shutdown would cool the Northern Hemisphere and decrease rainfall over Europe. It can also have an effect on El Nino.
Has AMOC weakened before?
-
According to a study, AMOC has been relatively stable until the late 19th century. But with the end of the little ice age in about 1850, the AMOC began to decline, and a more drastic decline began in the mid-20th century.
Why is the AMOC slowing down?
-
Global Warming: Global warming can cause a weakening of the major ocean systems of the world.
-
Melting of Glaciers: Researchers have found that a part of the Arctic’s ice called the “Last Ice Area” has also melted. The freshwater from the melting ice reduces the salinity and density of the water. Now, the water is unable to sink as it used to and weakens the AMOC flow.
-
Indian Ocean:
-
Indian Ocean may also be helping the slowing down of AMOC.
-
According to researchers, as the Indian Ocean warms faster and faster, it generates additional precipitation. With so much precipitation in the Indian Ocean, there will be less precipitation in the Atlantic Ocean, leading to higher salinity in the waters of the tropical portion of the Atlantic.
-
This saltier water in the Atlantic, as it comes north via AMOC, will get cold much quicker than usual and sink faster.
-