Cluster Munitions:
-
A cluster munition means a “conventional munition that is designed to disperse or release explosive submunitions each weighing less than 20 kilograms, and includes those explosive submunitions”.
-
Essentially, cluster munitions are non-precision weapons that are designed to injure or kill human beings indiscriminately over a large area, and to destroy vehicles and infrastructure such as runways, railway or power transmission lines.
-
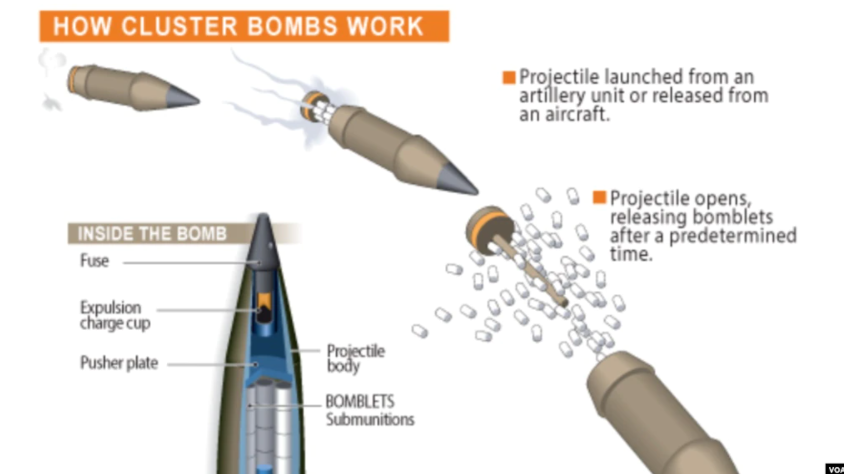
They can be dropped from an aircraft or launched in a projectile that spins in flight, scattering many bomblets as it travels.
-
Many of these bomblets end up not exploding, but continue to lie on the ground, often partially or fully hidden and difficult to locate and remove, posing a threat to the civilian population for long after the fighting has ceased.
-
The Convention on Cluster Munitions specifically identifies “cluster munition remnants”, which include “failed cluster munitions, abandoned cluster munitions, unexploded submunitions and unexploded bomblets”.
What is the Convention on Cluster Munitions?
-
The Convention on Cluster Munitions is a United Nations–adopted legal instrument that prohibits all use, production, transfer and stockpiling of cluster munitions.
-
It establishes a framework for cooperation and assistance to ensure adequate assistance to survivors and their communities, clearance of contaminated areas, risk reduction education and destruction of stockpiles.
-
It was adopted in Dublin, Ireland in 2008, and was opened for signature in Oslo, Norway.
-
It entered into force in 2010 after the requirement of 30 ratifications was complete.
-
Currently, the convention has 110 State Parties and 13 Signatory States.
-
Countries that ratify the convention are obliged to never use cluster munitions, and also to never develop, produce, otherwise acquire, retain, stockpile or transfer to anyone cluster munitions.
-
India has not signed the convention and is not a party to it. Other countries that are not parties are the US, Russia, China, Pakistan and Israel, among others.