-
Bird flu, also known as Avian influenza (AI), is a highly contagious viral disease affecting several species of food-producing birds (chickens, turkeys, quails, guinea fowl, etc.) as well as pet birds and wild birds.
-
Occasionally mammals, including humans, may contract avian influenza.
-
Types of Influenza Viruses:
-
Influenza viruses are grouped into three types; A, B, and C.
-
Only type A is known to infect animals and is zoonotic, meaning it can also infect humans.
-
Avian influenza virus subtypes include A(H5N1), A(H7N9), A(H9N2) and A(H10N3).
-
Type B and C mostly infect humans and typically cause mild disease.
-
-
Classification:
-
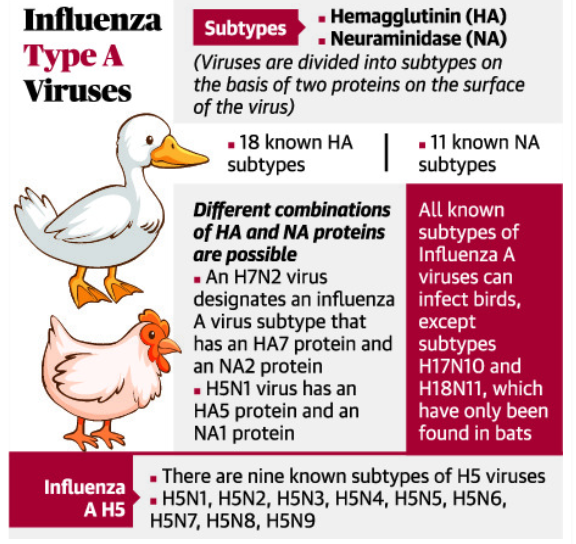
Influenza viruses are classified into subtypes based on two surface proteins, Hemagglutinin (HA) and Neuraminidase (NA).
-
For example, a virus that has an HA 7 protein and NA 9 protein is designated as subtype H7N9.
-
-
Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza (HPAI) A(H5N1) virus occurs mainly in birds and is highly contagious among them.
-
Impact:
-
Avian Influenza outbreaks can lead to devastating consequences for the country, particularly the poultry industry.
-
Farmers might experience a high level of mortality in their flocks, with rates often around 50%.
-
-
Prevention:
-
Strict biosecurity measures and good hygiene are essential in protecting against disease outbreaks.
-
-
Eradication:
-
If the infection is detected in animals, a policy of culling infected and contact animals is normally used in an effort to rapidly contain, control and eradicate the disease.
-
-
India’s Status:
-
Fresh cases of bird flu were reported in different states of India between December 2020-January 2021 causing alarm across the country.
-
Previously in 2019, India was declared free from Avian Influenza (H5N1), which had also been notified to the World Organization for Animal Health (OIE).
-
The OIE is an intergovernmental organisation responsible for improving animal health worldwide. It is headquartered in Paris, France.
-