Iron Dome System:
-
Iron Dome is a short-range, ground-to-air, air defence system.
-
It is developed by Israeli manufacturer Rafael Advanced Défense Systems with support from the United States.
-
Purpose:
-
It is used for countering rockets, artillery & mortars (C-RAM).
-
It can also counter aircraft, helicopters and unmanned aerial vehicles fired from distances of up to 70 kilometres.
-
-
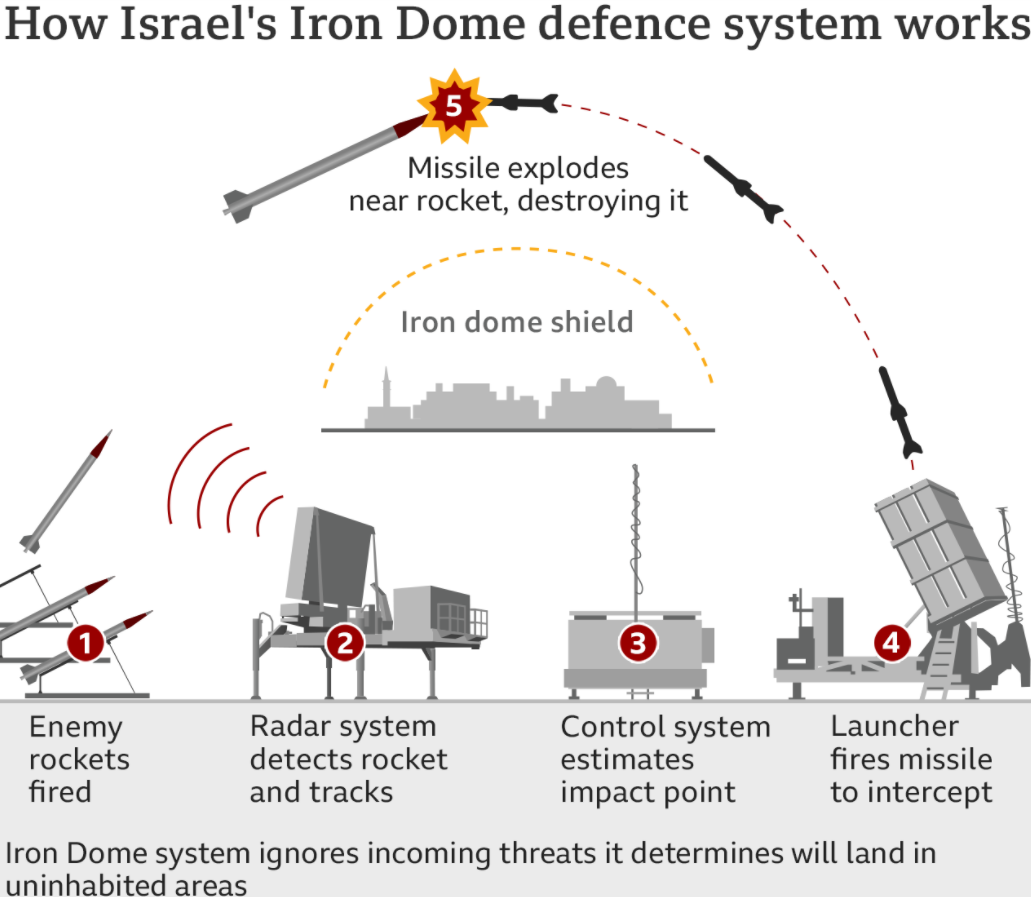
How does Iron Dome work? The Iron Dome has three main systems. These systems work together to provide a shield over the area where it is deployed, handling multiple threats:
-
Detection and tracking radar: It tracks any incoming threat into Israel
-
battle management and weapon control system (BMC): It predicts the incoming rocket’s trajectory
-
Tamir Interceptor Missiles: Information picked by the system is then used to guide Tamir interceptor missiles. These missiles are fired vertically either from mobile units or a static launch site. This will detonate the incoming rocket in the air by producing explosions in the sky.
-
-
The missile is capable of being used in all weather conditions, including during the day and night.
-
Israel claims the system has stopped thousands of enemy launches from hitting targets, with a success rate of more than 90%.