What is Pyrolysis?
-
Pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of materials at elevated temperatures in an inert atmosphere.
-
It involves a change in chemical composition. The word is coined from the Greek-derived elements pyro “fire” and lysis “separating”.
-
It is most commonly used in the treatment of organic materials. It is one of the processes involved in charring wood.
-
It is considered as the first step in the processes of gasification or combustion.
-
The process typically occurs at temperatures above 430 °C (800 °F) and under pressure.
-
It simultaneously involves the change of physical phase and chemical composition of organic material.
-
Pyrolysis is an irreversible process.
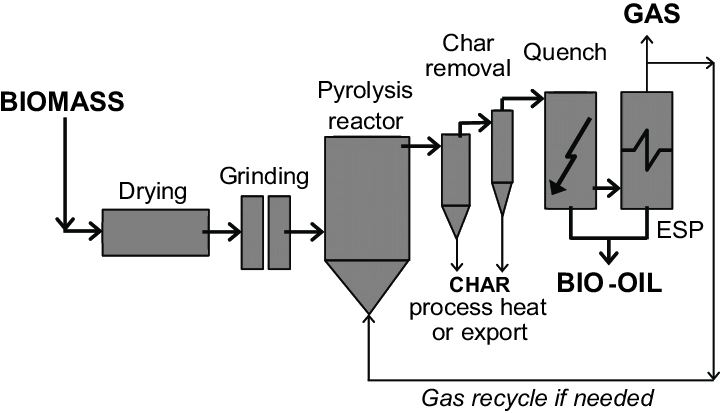
How does it work?
-
In general, pyrolysis of organic substances produces volatile products and leaves a solid residue enriched in carbon, char.
-
Extreme pyrolysis, which leaves mostly carbon as the residue, is called carbonization.
-
The process is used heavily in the chemical industry, for example, to produce ethylene, many forms of carbon, and other chemicals from petroleum, coal, and even wood, to produce coke from coal.