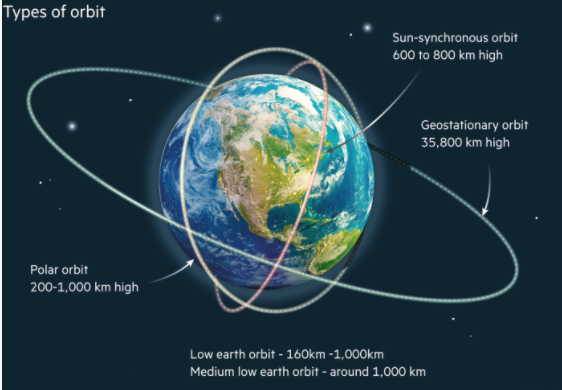
Geosynchronous Orbit
-
Geosynchronous satellites are launched into orbit in the same direction the Earth is spinning and can have any inclination.
-
When the satellite is in orbit at a specific altitude (approximately 36,000km above the Earth’s surface), it will exactly match the rotation of the Earth.
-
While, Geostationary orbits fall in the same category as geosynchronous orbits, but with that one special quality of being parked over the equator.
-
In the case of geostationary satellites, the Earth’s force of gravity is exactly enough to provide acceleration required for circular motion.
-
Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit(GTO): To attain geostationary or geosynchronous earth orbits, a spacecraft is first launched into a Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit.
-
From the GTO the spacecraft uses its engines to shift to geostationary or geosynchronous orbit.