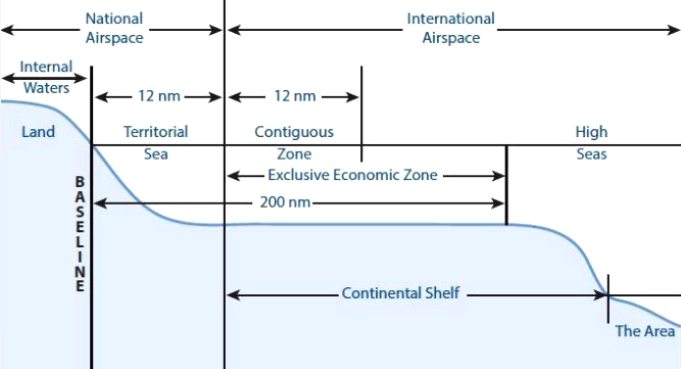
UN Convention of the Law of the Sea:
-
It is also called the Law of the Sea Convention or the Law of the Sea treaty
-
It is the international agreement that resulted from the third United Nations Conference on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS III), which took place between 1973 and 1982.
-
The Law of the Sea Convention defines the rights and responsibilities of nations with respect to their use of the world’s oceans, establishing guidelines for businesses, the environment, and the management of marine natural resources.
-
It divides marine areas into five main zones namely:
-
Internal Waters,
-
Territorial Sea,
-
Contiguous Zone,
-
Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) and
-
High Seas.
-
-
It is the only international convention which stipulates a framework for state jurisdiction in maritime spaces. It provides a different legal status to different maritime zones.
-
It provides the backbone for offshore governance by coastal states and those navigating the oceans.
-
It not only zones coastal states’ offshore areas but also provides specific guidance for states’ rights and responsibilities in the five concentric zones.
-
India has ratified UNCLOS.