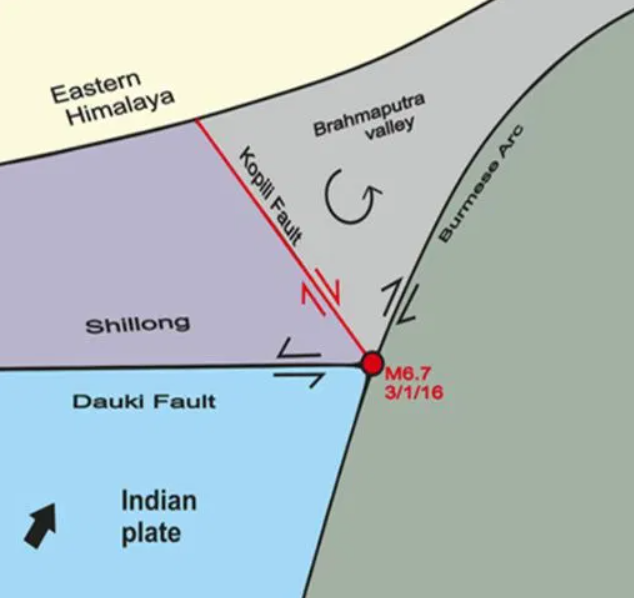
Kopili Fault Zone:
-
The Kopili fault zone is a 300-km northwest-southeast trending fault. It is extending from the western part of Manipur to the tri-junction of Bhutan, Arunachal Pradesh and Assam.
-
The National Centre for Seismology (NCS) has said that the tremors in Assam can be attributed to the Kopili Fault Zone.
-
A fault is a fracture or zone of fractures between two blocks of rock. Faults allow the blocks to move relative to each other. This movement may occur rapidly, in the form of an earthquake. Or it may occur slowly, in the form of creep.
-
Seismically Active: This zone is a seismically active area and falls into the highest Seismic Hazard Zone V.
-
The zone is associated with collisional tectonics because of the Indian Plate subducting beneath the Eurasian Plate.
-
Subduction is a geological process in which one crustal plate is forced below the edge of another.
-
Characteristics: Kopili fault zone and its neighbouring areas are characterised by alluvial soils. These alluvial soil have a higher potential of trapping seismic waves. Thus making the region the most earthquake-prone zone in North East India.
-
Earlier Earthquakes: Kopili fault zone has witnessed many seismic activities in the past. This includes the 1869 earthquake (7.8 magnitude) and the 1943 earthquake (7.3 magnitude).