Findings:
-
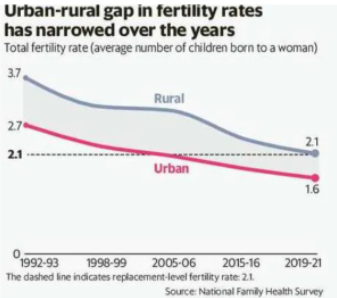
Total Fertility Rates (TFR): Declined from 2.2 to 2.0 at the national level. All Phase-II States have achieved replacement level of fertility (2.1) except Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Jharkhand and Uttar Pradesh.
-
Contraceptive Prevalence Rate (CPR): Increased from 54% to 67% at an all-India level and in almost all Phase-II States/UTs with an exception of Punjab.
-
Full immunization drive: Improved among children aged 12-23 months from 62% (NFHS-4) to 76% at an all-India level. This increase is attributed to the flagship initiative of Mission Indradhanush launched by the government since 2015.
-
Institutional births: Increased substantially from 79% to 89% at all-India levels. Institutional delivery is 100% in Puducherry and Tamil Nadu and more than 90 per cent in 7 States/UTs out of 12 Phase II States/UTs. There has also been a substantial increase in C-section deliveries in many States/UTs, especially in private health facilities.
-
Child Nutrition: When compares to NFHS-4,
-
1. Stunting – declined from 38.4% to 35.5%,
-
2. Wasting declined from 21% to 19.3%,
-
3. Underweight – declined from 35.8% to 32.1% and
-
4. Overweight – Increased from 2.1% to 3.4%.
-
Further, breastfeeding is also shown an improvement from 55% in 2015-16 to 64% in 2019-21.
-
-
Child marriage: Declined from 27% to 23% in the last five years. West Bengal and Bihar had the highest prevalence of girl child marriage, and this has remained unchanged since the NFHS-4.
-
Anaemia: More than half of the children and women (including pregnant women) are anaemic in all the phase-II States/UTs and all-India levels compared to NFHS4. Assam is among the worst-performing states, with a huge spike in anaemic cases.
-
Women’s empowerment: Significant progress has been recorded between NFHS-4 and NFHS-5 in regard to women operating bank accounts from 53% to 79% at an all-India level.