Cloud seeding:
-
Cloud seeding is a form of weather modification
-
It is a way of changing the amount or type of precipitation that falls from clouds
-
How? by dispersing substances into the air that serve as cloud condensation or ice nuclei, which alter the microphysical processes within the cloud
-
Why? The usual intent is to increase precipitation (rain or snow), but hail and fog suppression are also widely practiced in airports
-
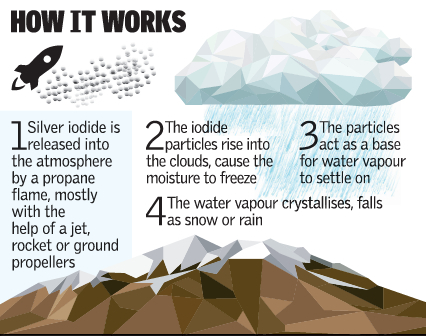
Chemicals used: In cloud seeding, either dry ice, or more commonly, silver iodide aerosols are sprayed into the upper part of clouds to try to stimulate the precipitation process and form rain
-
Cloud seeding also occurs due to ice nucleators in nature, most of which are bacterial in origin
-
Mechanism: Since most rainfall starts through the growth of ice crystals from super-cooled cloud droplets (droplets colder than the freezing point, 32 deg. F or 0 deg. C) in the upper parts of clouds, the silver iodide particles are meant to encourage the growth of new ice particles
-
The history of cloud seeding has experienced uncertain results because it can never be known whether a cloud that rains after seeding might have rained anyway
-
This is because seeding is performed on clouds that look like they have some potential for producing rain
Uses of Cloud seeding
-
In agriculture, crop loss can be prevented.
-
In water management, floods and droughts can be managed (Indonesia is known to use it to prevent risk of floods).
Cloud seeding in India
-
In India, Tamil Nadu became the first state in the country to attempt cloud- seeding as early as 1983-1984.
-
Karnataka and Maharashtra followed in 2003 and 2008 respectively when drought situations prevailed.
-
As Indian socio-economic setup is vitally linked with Monsoon (which is highly erratic leading to agrarian and economic crises), many states are experimenting in cloud seeding projects.
-
India has several drought-hit areas like in Bundelkhand in UP and elsewhere in Maharashtra and Karnataka.
-
The technology also has strategic applications, like for defence purposes. Over the past decade, many countries, especially China, have mastered it.